 |
| Medicine for infection |
The Need to Take Action
In her report, Davies mentioned that there have only been a handful of new antibiotics developed in recent years, and that further action is needed to combat the rise of so-called “superbugs.” She even went on to warn that routine medical procedures could become increasingly dangerous because a person may be at risk for going under the knife for something common, only to contract a fatal strain of antibiotic resistant virus.
MRSA Not the Only Problematic Virus
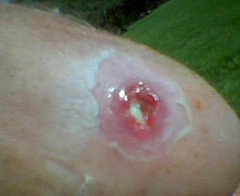
MRSA is one of the most widespread types of antibiotic resistant viruses, Both in Europe and the United States. Stateside, it’s said to be responsible for about 19,000 deaths per year, with similar numbers in Europe. MRSA is common in hospital environments, but recent developments have highlighted a strain of gonorrhea that also resistant to antibiotics. Although gonorrhea is a bacteria and not a virus, some health professionals say this new version of the sexually transmitted disease could quickly put a damper on bedroom activities unless an effective treatment is found.
Treatments Are Already Less Effective
It was once easy to manage gonorrhea cases with a shot of penicillin. However, MSNBC reported that scientists have noted how previously effective treatments don’t seem to have the same power as before. Now, gonorrhea responds best to a class of antibiotics called cephalosporins, and other types don’t work as well as in times past.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in the United States reports that most recent data indicates over 336,000 gonorrhea cases per year. Although this may seem like a large number, some health professionals say that it still falls far short. Regardless of precise numbers, gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported infectious disease in the United States.
Fighting Back Against Antibiotic Resistance: A Team Effort
Healthcare workers say that managing the problem of antibiotic resistance is something that both patients and providers can do together. From a patient perspective, it’s important to be proactive and ask healthcare professionals whether there are other methods of treatment besides antibiotics. Also, when antibiotics are prescribed, patients should only take them for the recommended duration, and not share the medication with others. On the other hand, healthcare workers can help prevent the spread by being careful not to over prescribe antibiotics, and also taking the proper measures to control identified instances of antibiotic resistance problems in healthcare settings.
Staying Safe, Every Time

If you’re worried about the risk of contracting this new type of gonorrhea, fortunately it’s no harder to prevent it now that it has been in previous years The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention mention that condoms reduce the occurrence of STDs like gonorrhea, as long as the products are used properly and consistently. Also, it’s very simple to gain peace of mind by visiting a testing center in your area. All strains of gonorrhea are problematic because they often don’t show symptoms right away. Rather than waiting for symptoms to show up, think about getting into the practice of regular sexual testing.
Whether you’re thinking uneasily about if you might be inviting a superbug into the bedroom, or just went to keep you and your partner as safe as possible during intercourse, simple measures are still worthwhile.
About the Author
Writer Karen Alton writes for health testing centers.